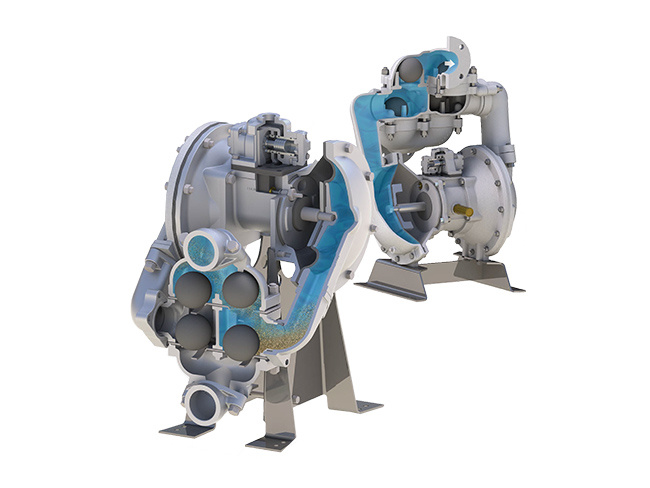
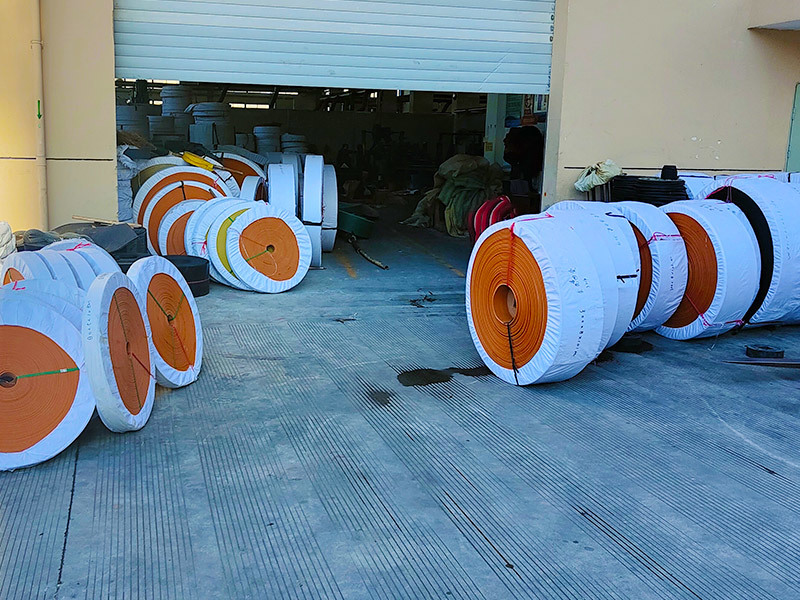
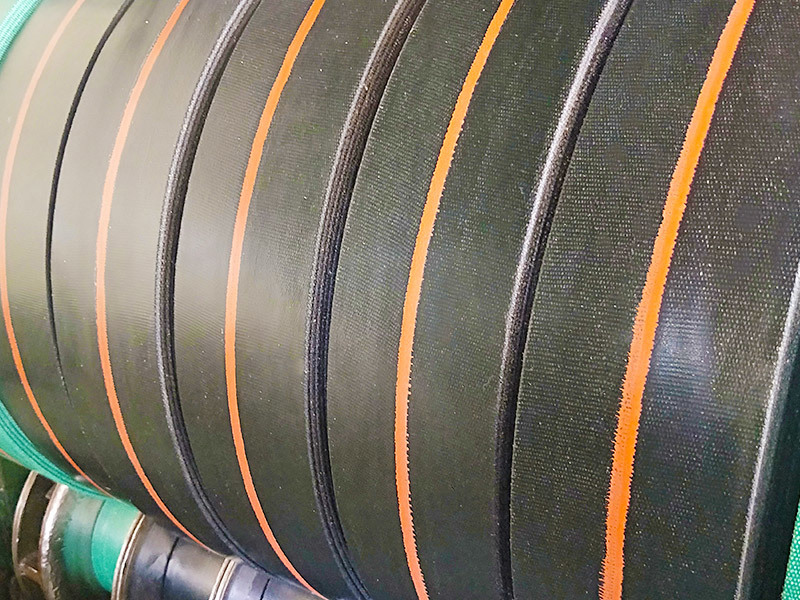
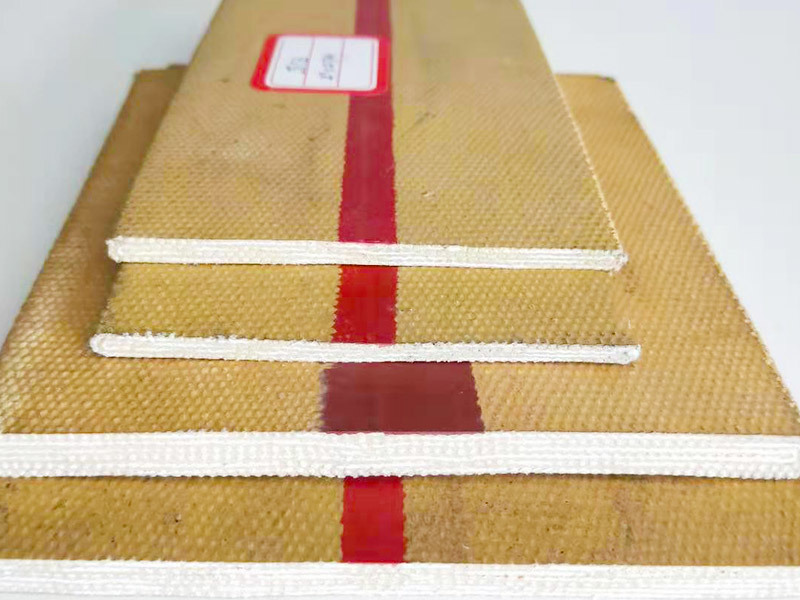
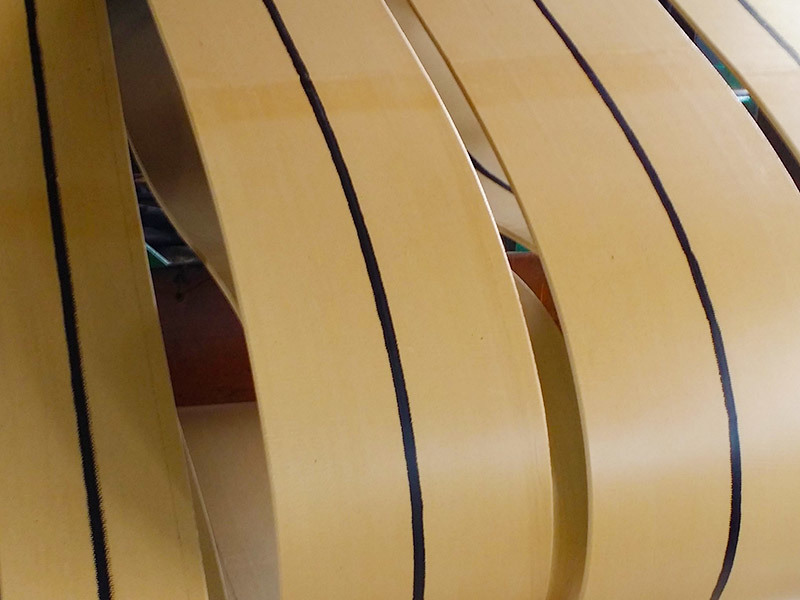
Rubber refers to a highly elastic polymer material that exhibits reversible deformation. It is elastic at room temperature and can undergo significant deformation under small external forces, returning to its original shape once the force is removed. Rubber is classified as a completely amorphous polymer, with a low glass transition temperature (Tg) and often a high molecular weight, typically exceeding several hundred thousand.
Rubber refers to a highly elastic polymer material that exhibits reversible deformation. It is elastic at room temperature and can undergo significant deformation under small external forces, returning to its original shape once the force is removed. Rubber is classified as a completely amorphous polymer, characterized by a low glass transition temperature (Tg) and often a high molecular weight, exceeding several hundred thousand. Rubber is divided into two types: natural rubber and synthetic rubber. Natural rubber is processed from the latex extracted from rubber trees, rubber grasses, and other plants; synthetic rubber is obtained through the polymerization of various monomers. Rubber products are widely used in various aspects of industry and daily life. Natural rubber is made from latex, which contains non-rubber components that remain in the solid natural rubber. Generally, natural rubber contains 92%-95% rubber hydrocarbons, while non-rubber hydrocarbons account for 5%-8%. Due to differences in manufacturing methods, origins, and even harvesting seasons, the proportions of these components may vary, but they generally fall within this range. Proteins can promote the vulcanization of rubber and delay aging. On the other hand, proteins have a strong hygroscopicity, which can cause rubber to absorb moisture and mold, leading to a decrease in insulation properties. Additionally, proteins have the disadvantage of increasing heat generation. Acetone extracts consist of certain fatty acids and sterols, some of which act as natural anti-aging agents and accelerators, while others help disperse powdered compounding agents during the mixing process and soften the raw rubber.
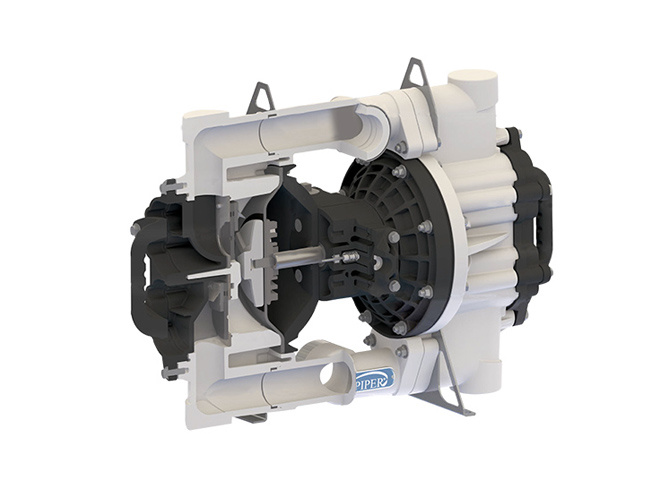
Rubber refers to a highly elastic polymer material that exhibits reversible deformation. It is elastic at room temperature and can undergo significant deformation under small external forces, returning to its original shape once the force is removed. Rubber is classified as a completely amorphous polymer, with a low glass transition temperature (Tg) and often a high molecular weight, typically exceeding several hundred thousand.
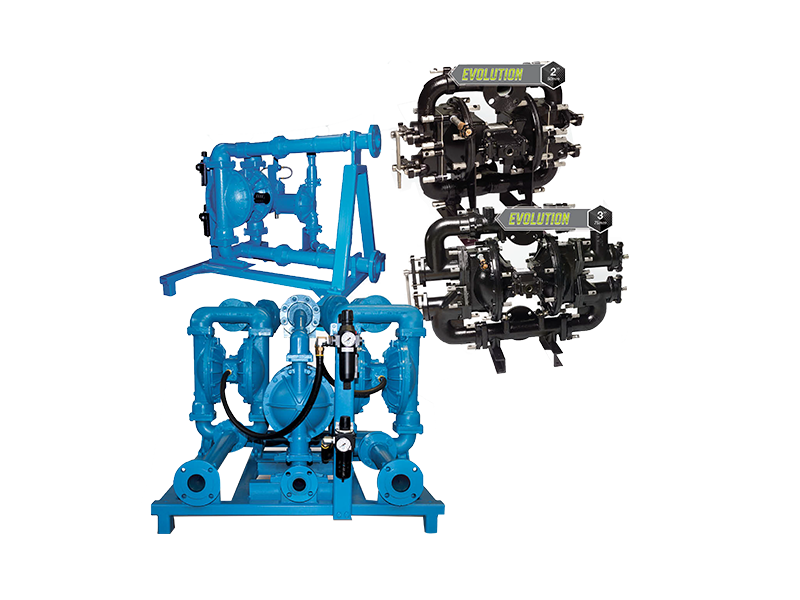
Rubber refers to a highly elastic polymer material that exhibits reversible deformation. It is elastic at room temperature and can undergo significant deformation under small external forces, returning to its original shape once the force is removed. Rubber is classified as a completely amorphous polymer, characterized by a low glass transition temperature (Tg) and often a high molecular weight, exceeding several hundred thousand. Rubber is divided into two types: natural rubber and synthetic rubber. Natural rubber is processed from the latex extracted from rubber trees, rubber grasses, and other plants; synthetic rubber is obtained through the polymerization of various monomers. Rubber products are widely used in various aspects of industry and daily life. Natural rubber is made from latex, which contains non-rubber components that remain in the solid natural rubber. Generally, natural rubber contains 92%-95% rubber hydrocarbons, while non-rubber hydrocarbons account for 5%-8%. Due to differences in manufacturing methods, origins, and even harvesting seasons, the proportions of these components may vary, but they generally fall within this range. Proteins can promote the vulcanization of rubber and delay aging. On the other hand, proteins have a strong hygroscopicity, which can cause rubber to absorb moisture and mold, leading to a decrease in insulation properties. Additionally, proteins have the disadvantage of increasing heat generation. Acetone extracts consist of certain fatty acids and sterols, some of which act as natural anti-aging agents and accelerators, while others help disperse powdered compounding agents during the mixing process and soften the raw rubber.
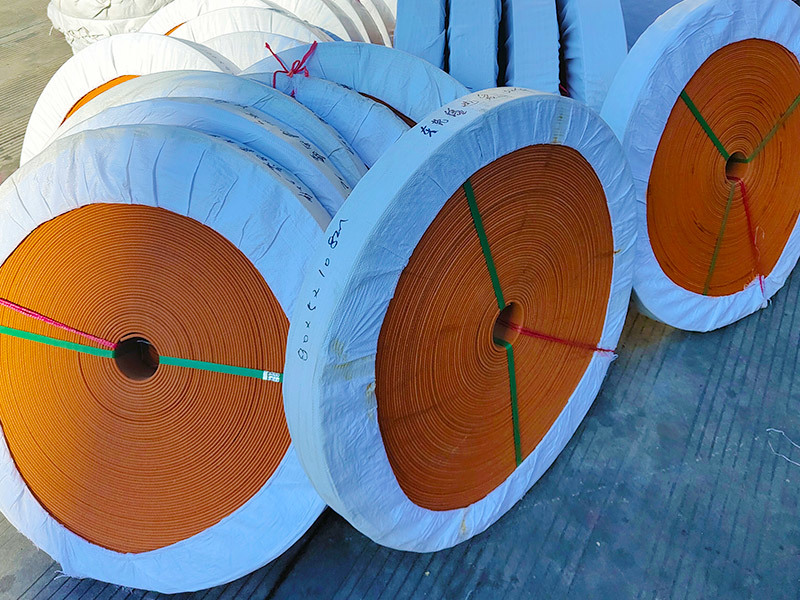
Rubber refers to a highly elastic polymer material that exhibits reversible deformation. It is elastic at room temperature and can undergo significant deformation under small external forces, returning to its original shape once the force is removed. Rubber is classified as a completely amorphous polymer, with a low glass transition temperature (Tg) and often a high molecular weight, typically exceeding several hundred thousand.
客服热线
关注我们
公众号

关注公众号 获取更多灵感
- 返回顶部